Deep Learning is on the rise, extending its application in every field, ranging from computer vision to natural language processing, healthcare, speech recognition, generating art, addition of sound to silent movies, machine translation, advertising, self-driving cars, etc. In this blog, we will extend the power of deep learning to the domain of music production. We will talk about how we can use deep learning to generate new musical beats.
The current technological advancements have transformed the way we produce music, listen, and work with music. With the advent of deep learning, it has now become possible to generate music without the need for working with instruments artists may not have had access to or the skills to use previously. This offers artists more creative freedom and ability to explore different domains of music.
Recurrent Neural Networks
Since music is a sequence of notes and chords, it doesn’t have a fixed dimensionality. Traditional deep neural network techniques cannot be applied to generate music as they assume the inputs and targets/outputs to have fixed dimensionality and outputs to be independent of each other. It is therefore clear that a domain-independent method that learns to map sequences to sequences would be useful.
Recurrent neural networks (RNNs) are a class of artificial neural networks that make use of sequential information present in the data.
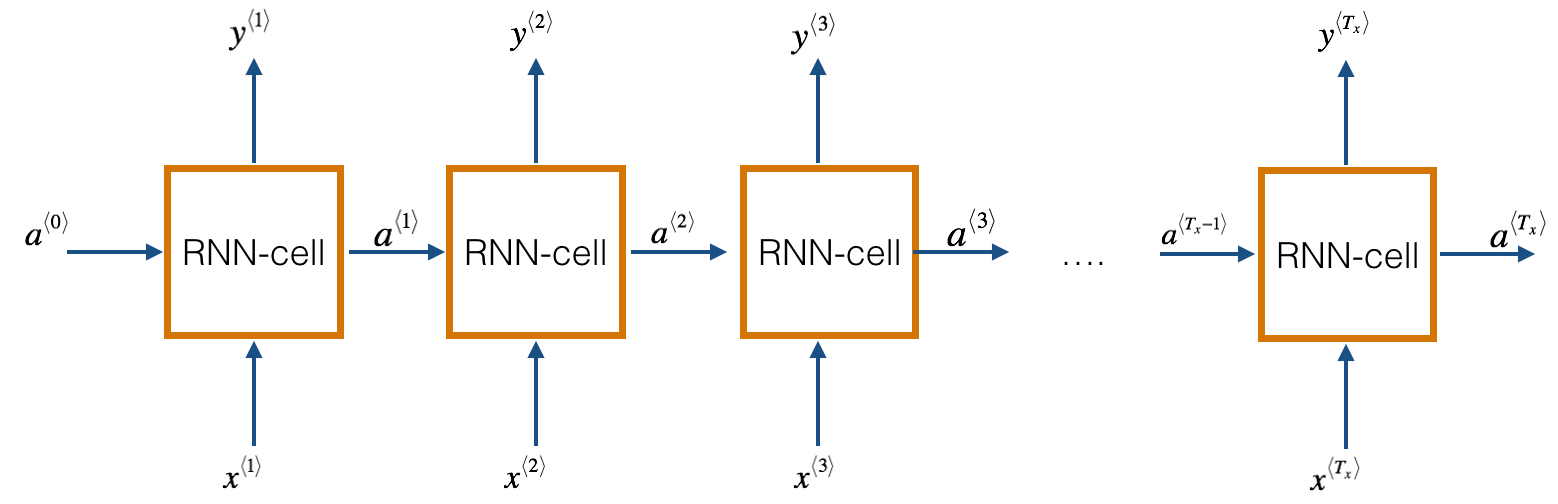
A recurrent neural network has looped, or recurrent, connections which allow the network to hold information across inputs. These connections can be thought of as memory cells. In other words, RNNs can make use of information learned in the previous time step. As seen in Fig. 1, the output of the previous hidden/activation layer is fed into the next hidden layer. Such an architecture is efficient in learning sequence-based data.
In this blog, we will be using the Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) architecture. LSTM is a type of recurrent neural network (proposed by Hochreiter and Schmidhuber, 1997) that can remember a piece of information and keep it saved for many timesteps.
Dataset
Our dataset includes piano tunes stored in the MIDI format. MIDI (Musical Instrument Digital Interface) is a protocol which allows electronic instruments and other digital musical tools to communicate with each other. Since a MIDI file only represents player information, i.e., a series of messages like ‘note on’, ‘note off, it is more compact, easy to modify, and can be adapted to any instrument.
Before we move forward, let us understand some music related terminologies:
- Note: A note is either a single sound or its representation in notation. Each note consist of pitch, octave, and an offset.
- Pitch: Pitch refers to the frequency of the sound.
- Octave: An octave is the interval between one musical pitch and another with half or double its frequency.
- Offset: Refers to the location of the note.
- Chord: Playing multiple notes at the same time constitutes a chord.
Data Preprocessing
We will use the music21 toolkit (a toolkit for computer-aided musicology, MIT) to extract data from these MIDI files.
-
Notes Extraction
def get_notes(): notes = [] for file in songs: # converting .mid file to stream object midi = converter.parse(file) notes_to_parse = [] try: # Given a single stream, partition into a part for each unique instrument parts = instrument.partitionByInstrument(midi) except: pass if parts: # if parts has instrument parts notes_to_parse = parts.parts[0].recurse() else: notes_to_parse = midi.flat.notes for element in notes_to_parse: if isinstance(element, note.Note): # if element is a note, extract pitch notes.append(str(element.pitch)) elif(isinstance(element, chord.Chord)): # if element is a chord, append the normal form of the # chord (a list of integers) to the list of notes. notes.append('.'.join(str(n) for n in element.normalOrder)) with open('data/notes', 'wb') as filepath: pickle.dump(notes, filepath) return notesThe function get_notes returns a list of notes and chords present in the .mid file. We use the converter.parse function to convert the midi file in a stream object, which in turn is used to extract notes and chords present in the file. The list returned by the function get_notes() looks as follows:
Out: ['F2', '4.5.7', '9.0', 'C3', '5.7.9', '7.0', 'E4', '4.5.8', '4.8', '4.8', '4', 'G#3', 'D4', 'G#3', 'C4', '4', 'B3', 'A2', 'E3', 'A3', '0.4', 'D4', '7.11', 'E3', '0.4.7', 'B4', 'C3', 'G3', 'C4', '4.7', '11.2', 'C3', 'C4', '11.2.4', 'G4', 'F2', 'C3', '0.5', '9.0', '4.7', 'F2', '4.5.7.9.0', '4.8', 'F4', '4', '4.8', '2.4', 'G#3', '8.0', 'E2', 'E3', 'B3', 'A2', '4.9', '0.4', '7.11', 'A2', '9.0.4', ...........]We can see that the list consists of pitches and chords (represented as a list of integers separated by a dot). We assume each new chord to be a new pitch on the list. As letters are used to generate words in a sentence, similarly the music vocabulary used to generate music is defined by the unique pitches in the notes list.
-
Generating Input and Output Sequences
A neural network accepts only real values as input and since the pitches in the notes list are in string format, we need to map each pitch in the notes list to an integer. We can do so as follows:
# Extract the unique pitches in the list of notes. pitchnames = sorted(set(item for item in notes)) # create a dictionary to map pitches to integers note_to_int = dict((note, number) for number, note in enumerate(pitchnames))Next, we will create an array of input and output sequences to train our model. Each input sequence will consist of 100 notes, while the output array stores the 101st note for the corresponding input sequence. So, the objective of the model will be to predict the 101st note of the input sequence of notes.
# create input sequences and the corresponding outputs for i in range(0, len(notes) - sequence_length, 1): sequence_in = notes[i: i + sequence_length] sequence_out = notes[i + sequence_length] network_input.append([note_to_int[char] for char in sequence_in]) network_output.append(note_to_int[sequence_out])Next, we reshape and normalize the input vector sequence before feeding it to the model. Finally, we one-hot encode our output vector.
n_patterns = len(network_input) # reshape the input into a format compatible with LSTM layers network_input = np.reshape(network_input, (n_patterns, sequence_length, 1)) # normalize input network_input = network_input / float(n_vocab) # One hot encode the output vector network_output = np_utils.to_categorical(network_output)
Model Architecture
We will use keras to build our model architecture. We use a character level-based architecture to train the model. So each input note in the music file is used to predict the next note in the file, i.e., each LSTM cell takes the previous layer activation (a⟨t−1⟩) and the previous layers actual output (y⟨t−1⟩) as input at the current time step tt. This is depicted in the following figure (Fig 2.).
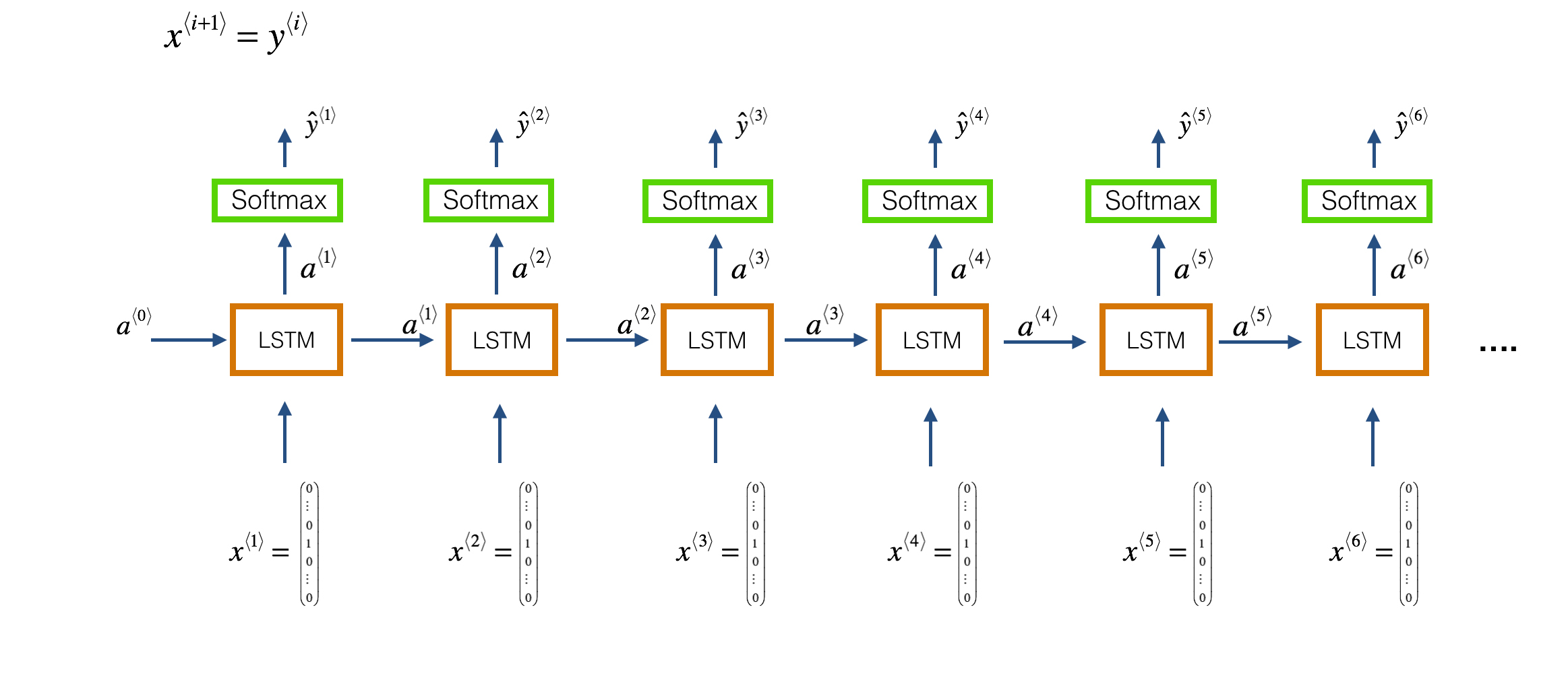
Our model architecture is defined as:
model = Sequential()
model.add(LSTM(128, input_shape=network_in.shape[1:], return_sequences=True))
model.add(Dropout(0.2))
model.add(LSTM(128, return_sequences=True))
model.add(Flatten())
model.add(Dense(256))
model.add(Dropout(0.3))
model.add(Dense(n_vocab))
model.add(Activation('softmax'))
model.compile(loss='categorical_crossentropy', optimizer='adam')
Our music model consists of two LSTM layers with each layer consisting of 128 hidden layers. We use ‘categorical cross entropy‘ as the loss function and ‘adam‘ as the optimizer. Fig. 3 shows the model summary.
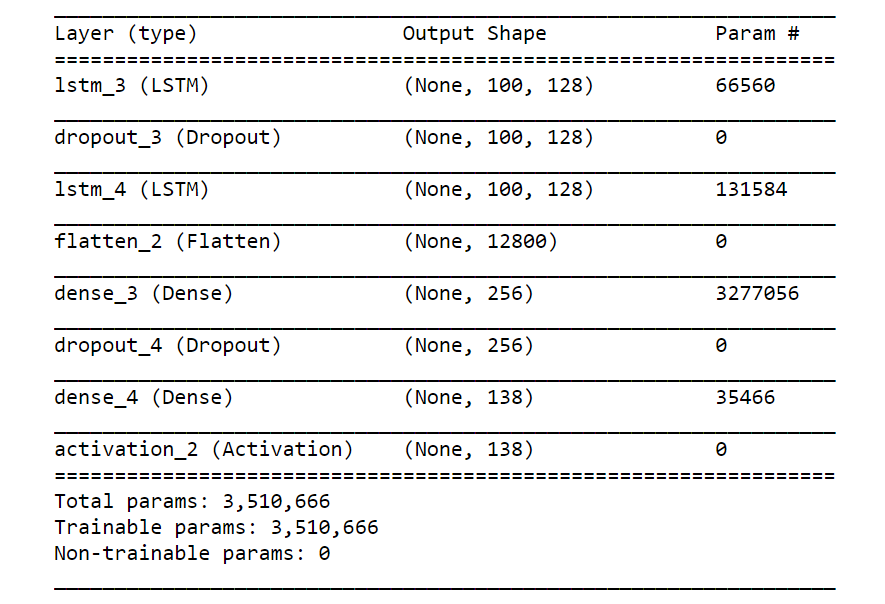
Model Training
To train the model, we call the model.fit function with the input and output sequences as the input to the function. We also create a model checkpoint which saves the best model weights.
from keras.callbacks import ModelCheckpoint
def train(model, network_input, network_output, epochs):
"""
Train the neural network
"""
filepath = 'weights.best.music3.hdf5'
checkpoint = ModelCheckpoint(filepath, monitor='loss', verbose=0, save_best_only=True)
model.fit(network_input, network_output, epochs=epochs, batch_size=32, callbacks=[checkpoint])
def train_network():
epochs = 200
notes = get_notes()
print('Notes processed')
n_vocab = len(set(notes))
print('Vocab generated')
network_in, network_out = prepare_sequences(notes, n_vocab)
print('Input and Output processed')
model = create_network(network_in, n_vocab)
print('Model created')
return model
print('Training in progress')
train(model, network_in, network_out, epochs)
print('Training completed')
The train_network method gets the notes, creates the input and output sequences, creates a model, and trains the model for 200 epochs.
Music Sample Generation
Now that we have trained our model, we can use it to generate some new notes. To generate new notes, we need a starting note. So, we randomly pick an integer and pick a random sequence from the input sequence as a starting point.
def generate_notes(model, network_input, pitchnames, n_vocab):
""" Generate notes from the neural network based on a sequence of notes """
# Pick a random integer
start = np.random.randint(0, len(network_input)-1)
int_to_note = dict((number, note) for number, note in enumerate(pitchnames))
# pick a random sequence from the input as a starting point for the prediction
pattern = network_input[start]
prediction_output = []
print('Generating notes........')
# generate 500 notes
for note_index in range(500):
prediction_input = np.reshape(pattern, (1, len(pattern), 1))
prediction_input = prediction_input / float(n_vocab)
prediction = model.predict(prediction_input, verbose=0)
# Predicted output is the argmax(P(h|D))
index = np.argmax(prediction)
# Mapping the predicted interger back to the corresponding note
result = int_to_note[index]
# Storing the predicted output
prediction_output.append(result)
pattern.append(index)
# Next input to the model
pattern = pattern[1:len(pattern)]
print('Notes Generated...')
return prediction_output
Next, we use the trained model to predict the next 500 notes. At each time step, the output of the previous layer (ŷ⟨t−1⟩) is provided as input (x⟨t⟩) to the LSTM layer at the current time step t. This is depicted in the following figure (see Fig. 4).
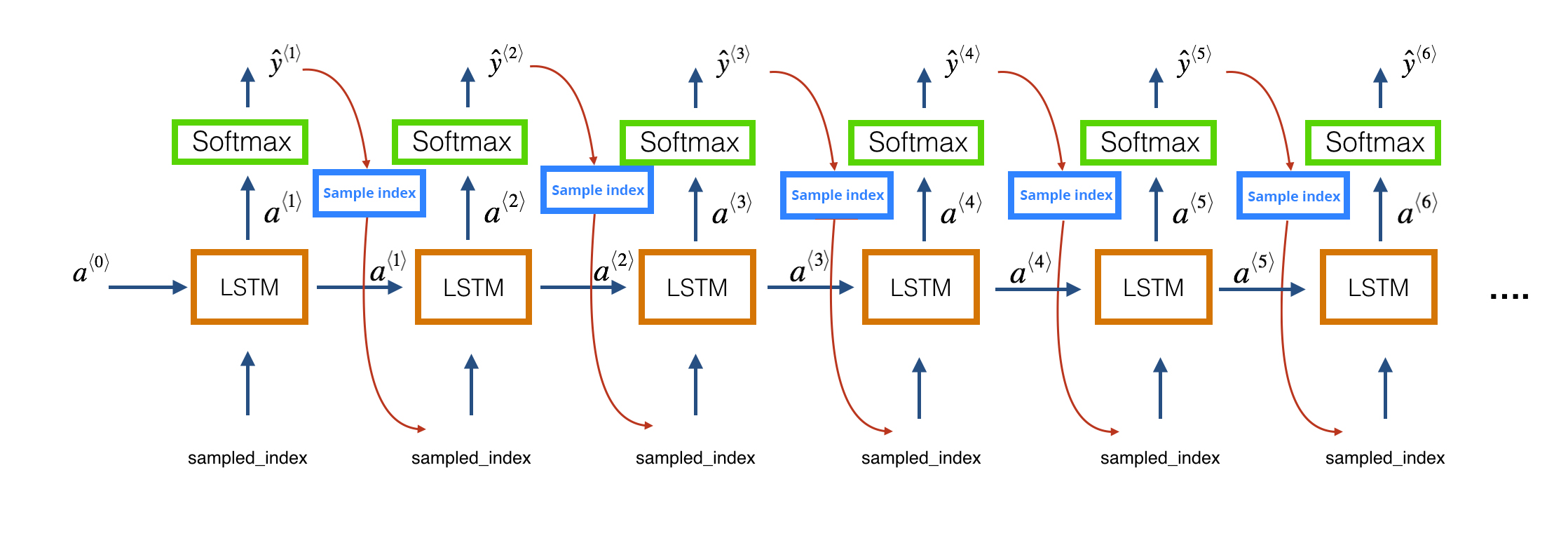
Since the predicted output is an array of probabilities, we choose the output at the index with the maximum probability. Finally, we map this index to the actual note and add this to the list of predicted output. Since the predicted output is a list of strings of notes and chords, we cannot play it. Hence, we encode the predicted output into the MIDI format using the create_midi method.
### Converts the predicted output to midi format
create_midi(prediction_output)
To create some new jazz music, you can simply call the generate() method, which calls all the related methods and saves the predicted output as a MIDI file.
#### Generate a new jazz music
generate()
Out:
Initiating music generation process.......
Loading Model weights.....
Model Loaded
Generating notes........
Notes Generated...
Saving Output file as midi....
To play the generated MIDI in the Jupyter Notebook you can import the play_midi method from the play.py file or use an external MIDI player or convert the MIDI file to the mp3. Let’s listen to our generated jazz piano music.
### Play the Jazz music
play.play_midi('test_output3.mid') 
Conclusion
Congratulations! You can now generate your own jazz music. You can find the full code in this Github repository. I encourage you to play with the parameters of the model and train the model with input sequences of different sequence lengths. Try to implement the code for some other instrument (such as guitar). Furthermore, such a character-based model can also be applied to a text corpus to generate sample texts, such as a poem.
Also, you can showcase your own personal composer and any similar idea in the World Music Hackathonby HackerEarth.
Have anything to say? Feel free to comment below for any questions, suggestions, and discussions related to this article. Till then, happy coding.






































 Our AI-enabled Smart Browser takes frequent snapshots via the webcam, throughout the assessment.
Consequently, it is impossible to copy-paste code or impersonate a candidate.The browser prevents the following
candidate actions and facilitates thorough monitoring of the assessment:
Our AI-enabled Smart Browser takes frequent snapshots via the webcam, throughout the assessment.
Consequently, it is impossible to copy-paste code or impersonate a candidate.The browser prevents the following
candidate actions and facilitates thorough monitoring of the assessment:











